The 10 Essential HR Metrics You Absolutely Need to Watch
HR metrics help you track key workforce activities to improve employee experience and HR effectiveness. Learn the most important HR metrics to track here.

Understanding business performance requires a comprehensive approach that goes beyond financial and sales data. People data, or HR data, is crucial for gaining insights into organizational health and opportunities for growth. That’s because it encompasses various HR metrics such as employee satisfaction, retention rates, training and development, diversity and inclusion, productivity, and performance evaluations.
In this article, you'll learn:
What are HR metrics?
Why do HR metrics matter?
How do I use HR metrics?
What are the 10 most important HR metrics?
2 advanced HR metrics to know

What are HR metrics?
Metrics are simply a way of assessing a particular area within a business. Within human resources, we measure categories of people metrics to understand how the organization’s biggest investment—its people—is faring, and how they affect the business. HR metrics help you track key workforce activities to improve employee experience, HR effectiveness, and ultimately, business performance.
There are a core set of HR metrics that every company should track to understand the impact that people have on the business, and that the business has on its people. In this post, we’ve outlined the ten most essential HR metrics to track.
Why do HR metrics matter?
HR metrics are data points that allow you to track key human resource and recruitment activities like employee performance, retention, compensation, engagement, cost-per-hire, time-to-hire, and more. This lets HR teams and people managers keep a close eye on how programs are functioning so that they can make adjustments if needed.
The way we work is constantly in flux. From the rapid shift to hybrid work to incorporating emerging technologies like generative AI into the workplace, HR is a forever-evolving and transforming field. HR metrics are a way of assessing a particular area within your business. They can also help you better face unforeseen events.
You need the ability to analyze workforce and people data to create an environment where people feel valued. If you don’t, you risk losing your employees’ trust and loyalty as their values shift and evolve.
Tracking essential HR metrics will help you connect people data with business outcomes to make data-informed decisions aligned with your company's goals.
"For every program that we have, we want to make sure that the programs are being optimized through data, that we’re being as impactful as we can, that we’re learning from our employees, what’s working and what’s not, and making quick course corrections. We also make sure that there are good metrics aligned with every initiative that we have so that we know how we’re tracking and how we can do better."
Scott Judd
Senior Director of People Analytics at eBay
How do I use HR metrics?
Use HR metrics to get a better view of what works and what doesn’t work in your company. To do so, start with a hypothesis or question. Here are some examples.
Is the voluntary turnover rate higher than you’d want?
How much is that costing you?
Is the talent acquisition process going well?
Or are you losing money on bad hires?
You can then turn to your HR tools to look for and analyze data that relate to those questions. These are only a few examples of what HR metrics can do for you.
Predicting future business needs is another area where HR analytics can be helpful. How many new employees will you need? What new skills will people need and want to learn? All of this can be answered using HR metrics and can help you make better business decisions.

What are the most important HR metrics?
There are several types of metrics, each with its role. Of them, we identified 10 core metrics any company must watch:
Headcount
Turnover
Diversity
Total cost of the workforce (TCOW)
Compensation
Spans and layers
Employee engagement
Talent acquisition
Learning
Workforce planning
If you want to go deeper, you can also track more advanced metrics such as productivity or manager effectiveness. We’ll talk about each metric in detail in the following section.
10 HR metrics you absolutely need to watch
1. Headcount
About 70% of an organization’s budget goes toward its people costs. Because of that, having an accurate headcount is crucial.
Headcount is the total number of people working in your company at any given time. This includes permanent, temporary, and contingent employees as well as gig workers.
The headcount tells you if you have enough people to accomplish your goals. It also allows you to forecast how that number may change. That means better financial management and a more effective estimation of costs.

View headcount in a year-to-date view to understand the net change in the organization.
2. Turnover
If you thought replacing employees was easy, think again. The process can sometimes cost one-half to twice the employee’s annual salary. This should be a good motivation to want to reduce turnover rates.
Metrics you need to know include:
Predicted resignation—an approximate number of people that will leave the company in the near future.
Resignation trends—are more or fewer people quitting now than in the past quarter? Can you spot any patterns?
Estimated replacement costs—how much will it cost to replace those who leave the company?
Resignation drivers—why do people leave the organization?
The turnover rate comprises voluntary and involuntary departures. But it is the voluntary turnover metrics that should get your attention.
You can control which contracts you terminate and which people you lay off. You don’t have the same control over their resignation. Analyzing this metric will help you understand the trends and the reasons behind the employee’s decision.
3. Diversity
A Harvard Business Review study showed that 76% of employees and job seekers look at diversity when considering a job offer.
What does diversity mean in a business context? It refers to the range of differences within the company, particularly related to race, gender, ethnicity, and age.
Diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging (DEIB) are becoming priorities in many organizations. But there’s still room for improvement.
Common DEIB metrics to track include:
Ethnicity
Gender
Location
Industry
The more diverse an organization is, the more chances it has of attracting top talent.
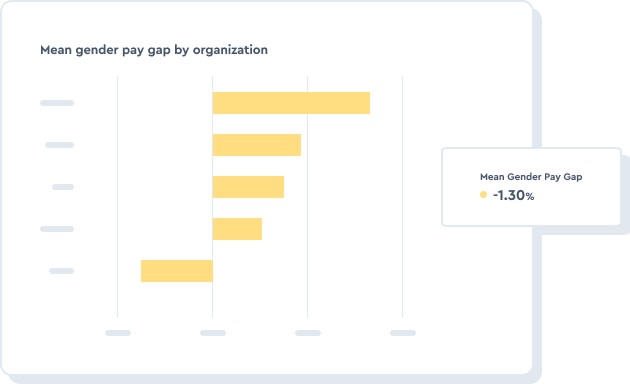
Examine the mean gender pay gap by organization to better understand pay equity in the business.
4. Total cost of workforce
The total cost of the workforce (TCOW) is more than salaries. It includes:
HR data such as headcount, salary, and benefits
Finance data such as workforce overheads
Market data
Knowing the TCOW helps you stay competitive by building an efficient workforce plan.
Metrics to watch include:
People: everything from recruitment, pay, onboarding, training, and retirement.
Overhead: how much does the company incur per employee?
Facilities: the cost of office spaces, equipment, and other utilities.

5. Compensation
Compensation is one of the top reasons people leave their jobs. It doesn’t just mean that the pay is too low. It might also mean that there are no advancement opportunities, or that people feel disrespected.
Compensation includes salaries, bonuses, paid time off, health insurance, retirement plans, and more. By tracking this metric, you make sure the pay scale is aligned with the market demand. Metrics to track include:
Salary
Compa-ratio
Range minimum, midpoint, and maximum
Range penetration
Grade or band
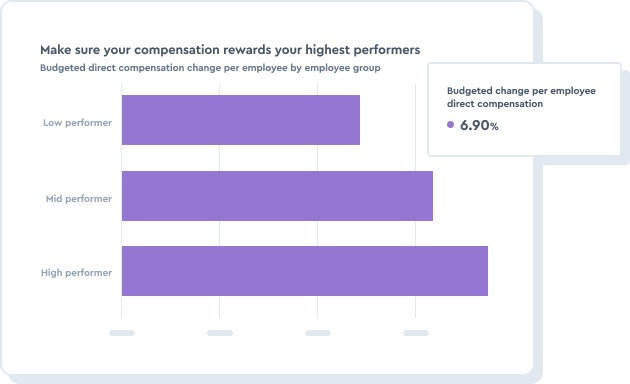
Look at the budgeted direct compensation changes to ensure your compensation plan rewards your highest performers.
6. Spans and layers
Organizations grow over time. By using the spans and layers metrics, your organization can reduce costs. Its employees can work together more effectively. These metrics also make it easier to assess salary grades and promotion opportunities.
Spans refer to the number of people who directly report to each manager. Layers refer to the number of supervisory levels.
Common spans and layers metrics to know include:
Productivity
Performance
Standardization of responsibilities
Types of work
Interdependency
Contingent layers
7. Employee engagement
Employees are a key component in any business. How well they relate to their employers, their colleagues, and the work they do are all part of the employee engagement metrics. In other words, this metric is about how connected and involved employees are in an organization.
Engaged employees are more productive. They tend to have lower rates of burnout and voluntary turnover.
Employee engagement metrics to track include:
Voluntary turnover
Absenteeism
Employee performance
Glassdoor reviews
Net promoter score (NPS) in feedback surveys.
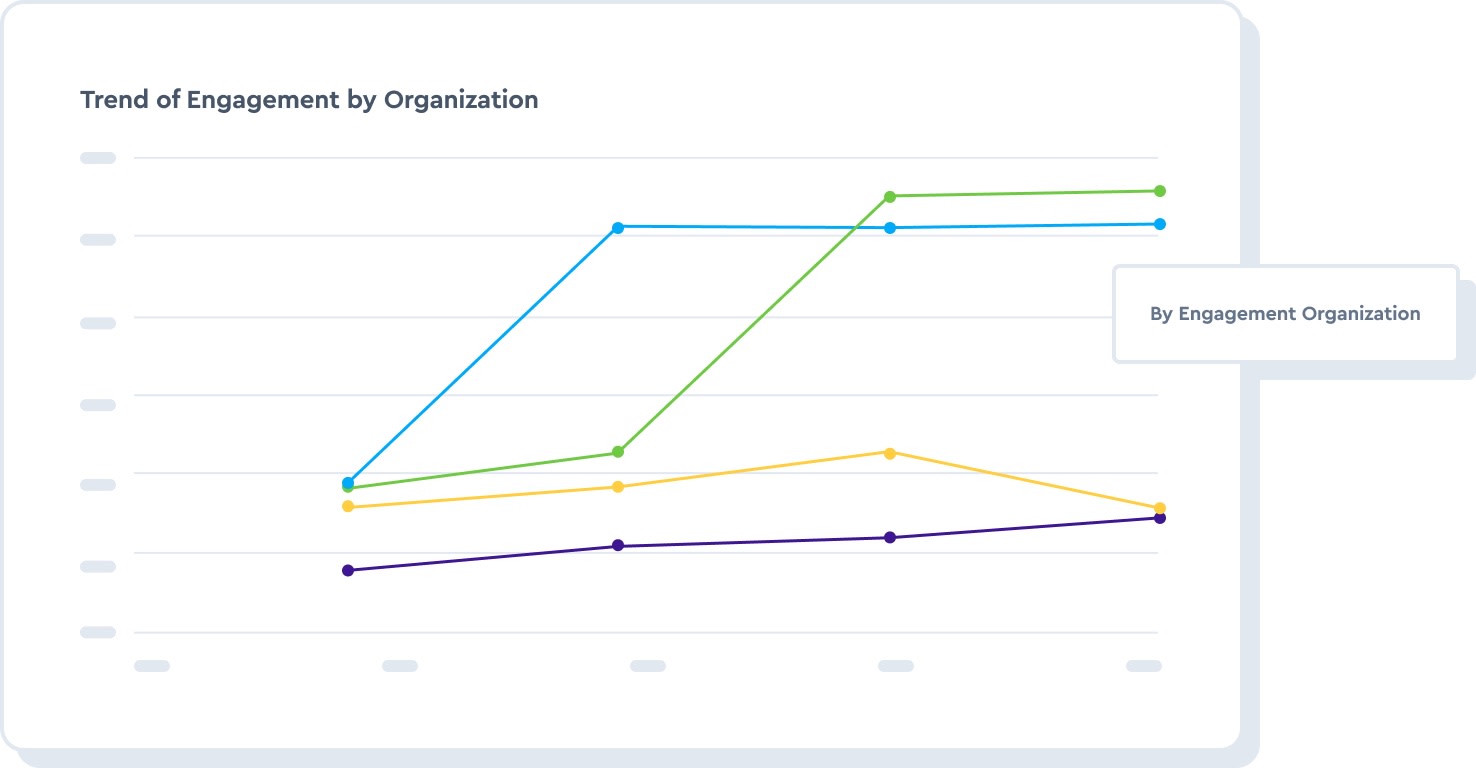
Empower people managers to see how engaged their teams are compared to the engagement trends of other organizations in the business.
8. Talent acquisition
A bad hire can cost you up to $240,000! Talent acquisition metrics may help prevent such a loss. They track how a person moves through the hiring process—from the job description to the offer and beyond.
By using this information correctly, you can make the right hiring decisions and avoid the huge costs of a bad choice.
Talent acquisition metrics to know include:
Revenue per employee
Quality of hire
Performance turnover in key jobs
Dollars of revenue lost due to position vacancy days
New hire failure rate
Applications per role
Diversity hires
9. Learning
People want to learn new things. So much so that 32% of those who changed jobs over the past years did so to learn a new skill.
Learning metrics track individual employees’ career development. They help reduce voluntary turnover and absenteeism. They improve engagement and individual performance.
Learning metrics to track include:
Skills that will be needed in the future
The trajectory of the current learning path
Internal hires/promotions
The baseline of skills present in the organization
10. Workforce planning
How many and what kind of workforce your organization needs during a period is part of workforce planning. These metrics allow you to identify gaps between the current workforce and your future needs.
Without these metrics, you risk lacking the necessary people to achieve your goals. Common metrics to know include:
Absenteeism
Attrition and turnover rates
Time to proficiency for new hires
Tenure, seniority, and experience levels
Skills coverage

See a breakdown of skills coverage in your organization to know where your gaps are and quickly put a plan in place.
2 advanced metrics to know
Productivity
Without a productive workforce, you’ll have a hard time doing anything in your organization. Productivity metrics refer to how much work a person can perform at any given time.
Common metrics include:
Revenue per employee
High performers
Average time to productivity
Manager effectiveness
Did you know effective managers make organizations "seven times more likely to innovate" and "6.7 times more likely to be agile?"
Effective managers directly impact the success of the business through how they lead their people. Common metrics of manager effectiveness include:
Manager engagement score
High performer resignation rate
Promotions actioned

HR metrics FAQ
What are HR metrics?
HR metrics are key data points that organizations use to track the effectiveness of their human resources and recruitment programs.
What are the most common metrics used by HR?
The most common metrics used by HR include headcount, turnover, diversity, compensation, the total cost of workforce spans and layers, employee engagement, talent acquisition, learning, workforce planning, productivity, and manager effectiveness.
Why are HR metrics important?
HR metrics are important because they give human resource and recruitment leaders objective insights into how to improve their programs. Without HR metrics, HR departments would be in the dark about how their workforce is performing, and how they can improve.
More about HR metrics
There's a core set of metrics every company should track. We’ve outlined 10 categories of basic HR metrics to know with five bonus metrics for building a more advanced people analytics practice and questions to ask genAI about each metric. Get the guide.
How to use people analytics metrics to better understand how the sales function impacts the business. Are you tracking these 15 sales function metrics?
Savvy CHROs track HR metrics to connect people data to business opportunities, identify potential roadblocks, and make strategic decisions fast. These are the 12 metrics every CHRO needs to track.
Employee retention metrics empower you to understand and prevent turnover, foster a thriving workforce, and maintain a competitive edge. Start with these seven employee retention metrics.